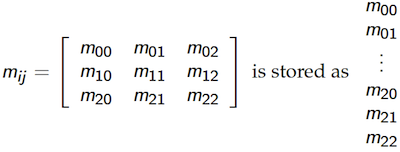Fortran and C/C++
BLAS / LAPACK routines are written in Fortran 77.
Difference between C and Fortran:
- The way matrices are stored in memory
- we have to transpose our matrices before we can pass them to a Fortran routine.
- The way arguments are passed to a subroutine.
- In Fortran the argument is passed to the routine and the routine can read and change this value. (call by reference)
- In C a copy of the value of the argument is passed to the routine and not the argument itself, the subroutine can't change the value of the argument. (call by value)
- To use call by reference in C, we have to pass pointers to variables instead of the variables themselves to the routine.
Arrays in Fortran / C
2D array (matrix) in C is defined as
double matrix[10][10];
In Fortran,
Real*8 matrix(10,10)
These 2D-array(matrix) are allocated in the 1D-memory (RAM) address space, however, the way of this is deferent in C and Fortran.
In C,
In Fortran
How arguments passed in Fortran / C
In Fortran, if make a value change in subroutine, the value in the main routine changes.
To do 'call by reference' in C, send pointers.
mysub(&a,&b,&c); : } void mybud(double *x,double *y,double *z){ : }
Fortran subroutine names from C
Lower case, put “_” in end.
For example, fortran subroutine
DNRM2(n,x,m,nm)
is :
dnrm2_(&n,x,&m,&nm);
when calling from C program.
Last modified
11 years ago
Last modified on 05/15/15 11:57:55
Attachments (3)
- 2D_Array_C.png (23.4 KB ) - added by 11 years ago.
- 2D_Array_Fortran.png (24.1 KB ) - added by 11 years ago.
- 700px-Subroutine_Arg.png (34.5 KB ) - added by 11 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip
Note:
See TracWiki
for help on using the wiki.